Generator Sizing and Load Management
Losing power during a storm or outage can be stressful, especially when you're worried about spoiled food, no heat or air conditioning, and losing connection to the outside world. A home standby generator can provide peace of mind by automatically keeping your essential systems running.
Here's everything you need to know about choosing the right size generator for your home.
Step 1: Identify What You Need to Keep Running
Before shopping for a generator, make a list of what's truly essential during a power outage. Consider these categories:
Must-Have Items
- Refrigerator and freezer - Keep food fresh and prevent spoilage
- Heating and cooling systems - Stay comfortable and safe
- Essential lighting - Navigate your home safely
- Water pump - Maintain water pressure (if you have a well)
- Sump pump - Prevent basement flooding
- Medical equipment - Critical for health and safety
Nice-to-Have Items
- Water heater - Hot water for showers and cleaning
- Washing machine and dryer - Continue laundry routines
- Dishwasher - Maintain kitchen cleanliness
- Pool pump - Keep pool water circulated
- Security system - Maintain home protection
- Internet and TV - Stay connected and entertained
Step 2: Calculate Your Power Requirements
Every electrical device uses power measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). Here's how to find this information:
- Check the appliance label - Look for a sticker or plate with electrical specifications
- Consult the user manual - Power consumption is usually listed in the specifications section
- Use online resources - Many manufacturers provide power consumption data on their websites
Common Appliance Power Usage
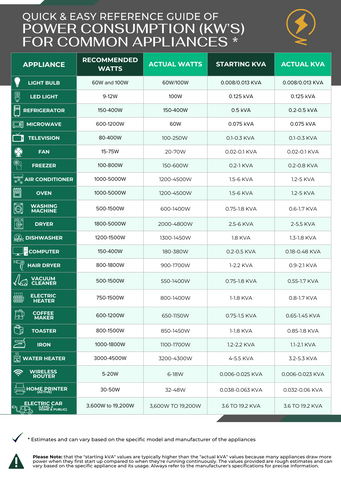
Important: Account for Startup Power
Many appliances need extra power when they first turn on - this is called "surge" or "starting" power. For example, your air conditioner might normally use 3,500 watts but needs 7,000 watts for the first few seconds when it starts up. Make sure to include these surge requirements in your calculations.
Step 3: Choose Your Generator Size
Home standby generators typically range from 7kW to 150kW. Here's a general sizing guide:
- 13kW: Essential items only (lights, refrigerator, some heating/cooling)
- 17-20kW: Most household needs including one major appliance at a time
- 25kW+: Whole house coverage including multiple large appliances simultaneously
Smart Money-Saving Option: Load Management
Here's where many homeowners can save thousands of dollars while still staying comfortable during outages.
What is Load Management?
Load management is like having a smart traffic controller for your electricity. When your generator is running multiple appliances and getting close to its limit, the load management system automatically turns off less critical items to prevent overloading.
How It Works
Let's say you have a 20kW generator and two air conditioning units that each use 5kW. Normally, you'd need a 30kW generator to run both at the same time. But with load management:
- Both A/C units are connected to the load management system
- Only one runs at a time - when one shuts off, the other can turn on
- Your home stays comfortable while using a smaller, less expensive generator
- You save thousands compared to buying a larger generator
Note: Your A/C units can be connected to built-in load management with a low-voltage connection and no need for optional accessories. Ovens, clothes dryers, and electric hot water heaters will require an optional load management module like this one from Cummins:

Load management systems typically control:
- Air conditioning units - Alternates between multiple units
- Electric ovens - Temporarily shuts off during peak demand
- Clothes dryers - Delays operation when other high-power items are running
- Water heaters - Briefly pauses heating during high demand periods
The Bottom Line
A 20kW air-cooled generator with load management can often handle the same essential needs as a 30kW liquid-cooled generator, but at a much lower cost. You'll still stay comfortable - you just won't run every high-power appliance at exactly the same moment.
Making Your Decision
Consider these questions when choosing your generator:
- What's your budget? An air-cooled generator with Intelligent Load Management can significantly reduce costs
- How critical is simultaneous operation? Can you live with one A/C unit at a time?
- What are your true essentials? Focus on safety and comfort rather than convenience
- Do you have special needs? Medical equipment or well pumps may require dedicated power
Next Steps
Once you've determined your power needs:
- Consult with a certified installer - They can verify your calculations and recommend the best solution
- Consider your fuel source - Natural gas, propane, or diesel
- Plan for installation - Proper placement and electrical connections are crucial
- Schedule regular maintenance - Keep your generator ready when you need it most
Remember, the goal isn't to power everything in your home simultaneously - it's to maintain safety, comfort, and essential functions during an outage. With smart planning and possibly load management, you can achieve this goal while staying within your budget.
The Cummins RS20AC Kit with transfer switch is an economical solution because it can manage up to four loads while providing a managed whole house solution for many homes up to 3,000 square feet.
Need expert help on generator sizing? Call one of our generator experts at Buckeye Power Systems at 901-379-8097.
